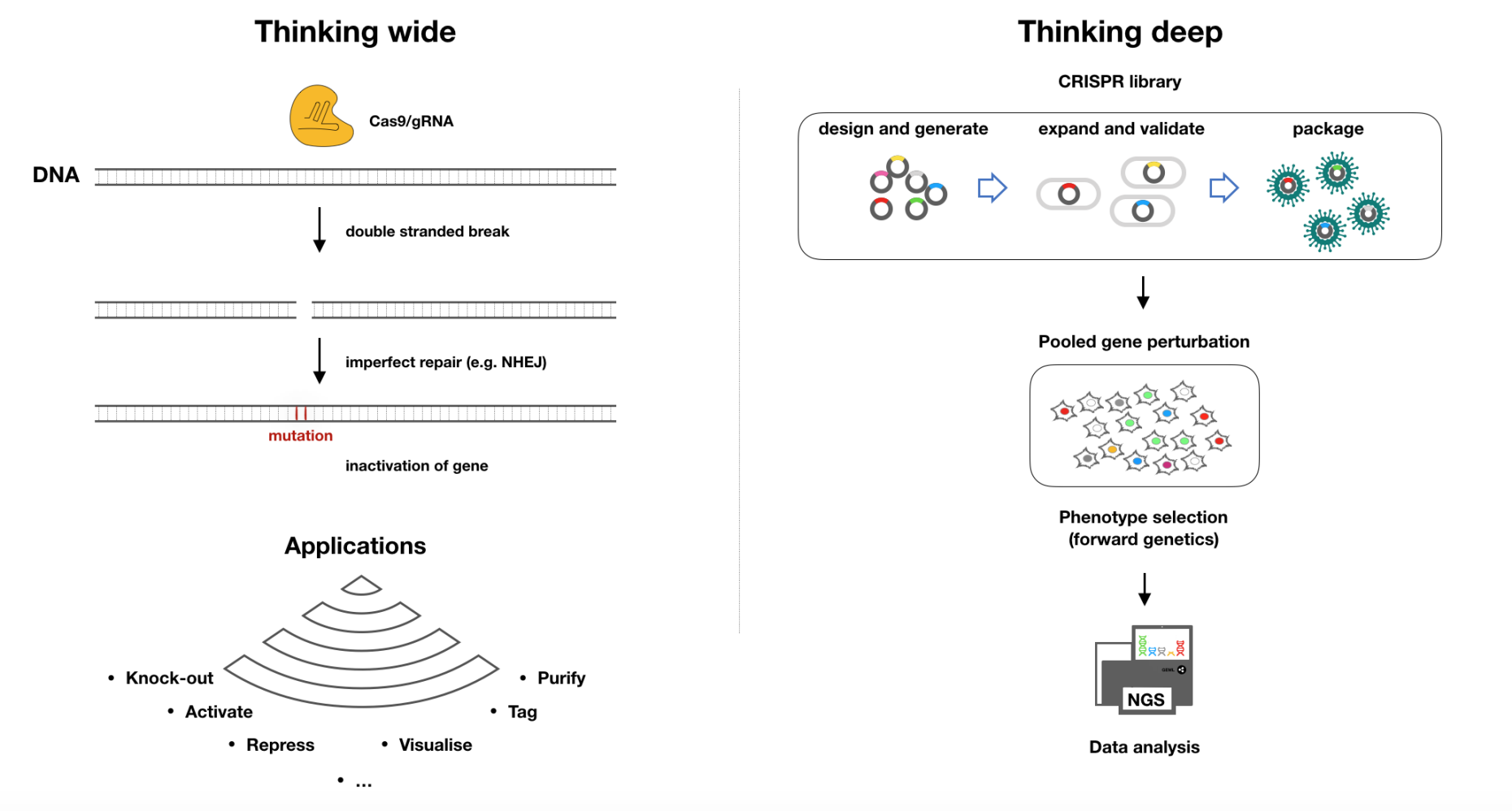
CRISPR Technology
Using the sequence information stored in a guide-RNA, proteins with nuclease activity can be targeted to a specific locus in the genome and induce a double stranded DNA break. Imperfect repair of that double stranded break can lead to inactivation of the targeted gene.
Using the same principle one can target a wide range of enzymatic activities with presision on the genome.
The versatility of the CRISPR/Cas system can be exploited to target thousands of genes in parallel in a pool of cells. The guide molecules can be used as tags to extrapolate the targeted gene retrospectively. Their enrichment or depletion, measured by deep Sequencing, serves as a proxy for identifying candidate genes.